HGH Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment

HGH deficiency in adults is a leading cause of depression, fatigue, weight gain, poor health, and sexual dysfunction. Receiving a diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency (GHD) is a relief for many men and women who have no idea what is wrong with them.
Frustrated with doctors who tell them to get used to aging, or others who dismiss their symptoms, many have run out of places to turn. Greenberg Health is here to tell you that your symptoms are not all in your head, although the cause might be.
When it comes to growth hormone deficiency, adults experience the effects differently from children who undergo slow growth. Due to the many varied functions of growth hormone (GH) in the body, the symptoms can confound and confuse doctors and laypeople alike. That is why you want to speak with a hormone specialist who understands the effects of HGH deficiency on the adult body.
Here are some growth hormone deficiency facts pertaining to adults:
- GHD in adults may be congenital, acquired, or idiopathic
- Declining growth hormone levels can affect people physically, physiologically, mentally, sexually, and emotionally
- People who were diagnosed with childhood-onset GHD may still require treatment as adults
- GHD is easily treated
- HGH therapy is safe, legal, and effective
HGH deficiency in adults is a leading cause of depression, fatigue, weight gain, poor health, and sexual dysfunction.
Causes of Adult HGH Deficiency
Just as the symptoms of low growth hormone levels can vary significantly, so can the HGH deficiency causes. We previously mentioned that GHD may be congenital, acquired, or idiopathic. It is time to take a closer look at why some adults suffer from declining GH levels.
Growth hormone deficiency causes in adults:
- Congenital:
The issue was present from birth, and may be due to any of the following:- Genetic mutations
- Structural defects in the brain
- Acquired:
The issue was not present at birth, and appeared at a later date:
- Head trauma
- Tumor of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- Treatment including radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery for the tumor or any other head issue
- Pituitary or hypothalamic disease
- Sarcoidosis
- Tuberculosis
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis
- Certain medical conditions or infections
- Poor blood supply to the brain
- Hormonal imbalance
- Idiopathic:
The issue arises from no known cause, including:
- Age-related hormone decline
- Not enough sleep to support GH release
- High levels of stress that interfere with GH production
- Sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise which promotes GH secretion during the day
- Weight gain which lowers GH levels
- Unhealthy dietary choices leading to weight gain
Many adults will find no known basis for their HGH deficiency. While it is not an inherited condition, some people may be more prone to GH decline if their parents appeared to experience early aging. Lifestyle habits can play a significant role in hormonal imbalance, especially in people who are overweight, highly stressed, or lead a sedentary life.
How Does HGH Deficiency Affect Adults
One of the problems with diagnosing HGH deficiency in adults is the variety of symptoms and lack of consistency. Unlike the common cold, which carries symptoms such as a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, and coughs, or the flu, which has body aches and fever, HGH deficiency symptoms are so vast that most people have only some of them – not all.
What that means is that one person with HGH deficiency may exhibit weight gain, fatigue, mood swings, lack of focus, and frequent illness. Another individual may report low libido, muscle loss, achy joints, and thinning hair. While the symptoms are different, the cause is the same.
The chart below highlights the most common symptoms of adult HGH deficiency:
Fatigue | Weight gain | Mood swings |
Depression | Decreased bone density | Joint pain |
Stiffness | Muscle loss | Reduced strength |
Anxiety | Lethargy | Poor heart health |
High cholesterol | Insulin resistance | Elevated blood pressure |
Muscle aches | Low libido | Vaginal dryness (females) |
Erectile dysfunction (males) | High blood sugar | Wrinkles |
Sagging skin | Dry skin | Age spots |
Thinning hair | Loss of hair color | Balding or hair loss |
Brittle nails | Irritability | Decreased motivation |
Lack of productivity | Social isolation | Poor focus |
Memory loss | Impaired cognitive processing | Hot and cold sensitivity |
Frequent illness | Slow healing | Reduced exercise capacity |
HGH deficiency also carries with it certain health risks that inherently increase in nature:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Cardiovascular disease
- Poor circulation
- Atherosclerosis
- High blood pressure
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Osteoporosis
- Dementia
- Depression
Adult HGH deficiency can increase the risk of many health conditions.
How Do Doctors Diagnose HGH Deficiency?
The diagnosis of HGH deficiency in adults differs considerably from that in children. Most adults do not have to go through the HGH deficiency test that stimulates GH secretion. That diagnostic tool is mainly for children with short stature.
Instead, hormone specialists run a growth hormone deficiency blood test that measures insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels in the blood. IGF-1 is a hormone secreted by the liver in a direct response to how much growth hormone it receives. Unlike GH, which enters the bloodstream in pulsatile bursts every few hours, IGF-1 levels remain constant throughout the day. Because growth hormone rapidly enters and exits the blood, it is a poor diagnostic marker to check.
The complete process for a growth hormone deficiency diagnosis is as follows:
- Consultation – during the medical consultation, patients describe their symptoms, state of health, and any concerns. They can ask questions about HGH deficiency and discuss their issues confidentially with a hormone specialist.
- Blood Test – blood analysis measures a variety of serum levels, assessing blood count, lipids and glucose, various hormones, and thyroid functions. The doctor will be able to rule out many other medical issues while diagnosing growth hormone deficiency.
- Physical Examination – the exam portion of the process allows for the gathering of information critical to determining how much HGH to prescribe. The medical examination also helps rule out other health issues while ensuring the individual is a candidate for HGH therapy.
- Health History Review – the medical questionnaire enables a person to provide complete details of all prior and current health issues. Listing of all prescription and over-the-counter medications, supplements, and vitamins is also necessary.
Following the completion of the above steps, the doctor can then determine if HGH deficiency is the cause of the symptoms.
Treatment Options for Adults with HGH Deficiency
Following a diagnosis of HGH deficiency, treatment can take one of the following two forms depending on the severity of the growth hormone decline:
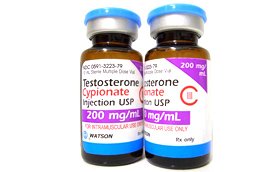
- HGH therapy – the most common form of treatment for HGH deficiency in adults, HGH therapy utilizes recombinant human growth hormone injections. Supplemental HGH provides the body with an adequate supply of bioidentical hormones to make up for what is lacking. Recombinant HGH contains the same 191 amino acid single chain as pituitary growth hormone. The body’s growth hormone receptors view it as the same, allowing for immediate cellular binding and usage.
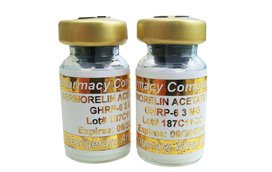
- Secretagogues – unlike HGH therapy, which directly increases growth hormone levels, the secretagogues ipamorelin and sermorelin target the hypothalamus or pituitary gland to stimulate growth hormone production. The result is an increase in GH secretion that occurs gradually over a period of months.
The pros and cons of HGH and secretagogue therapies area as follows:
- HGH pros: fast results, immediate increase in growth hormone levels
- HGH cons: higher cost, increased risk (although slight) of side effects
- Secretagogue pros: lower cost, natural increase in growth hormone production, fewer side effects
- Secretagogue cons: slow results, does not provide immediate increase in GH levels
Some people may utilize a combination approach to their treatment of HGH deficiency. The use of HGH therapy for a short time to bring about rapid benefits while also taking secretagogue injections to promote better GH production can help lower the overall cost by reducing the need for long-term HGH injections.
To learn more about treatment for adult HGH deficiency, please contact Greenberg Health. Our medical advisors are here for free, confidential consultations by phone during our regular business hours. Call or complete the form on this page for more information or to schedule blood testing.


















 Norditropin
Norditropin