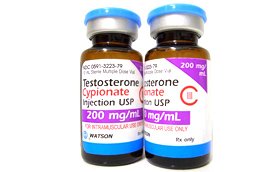
Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism

Hypogonadism is the term for Low T, a condition that can be described as the failure of the testes to produce either the androgen hormone (testosterone) or sperm – and, in some cases, both.
As a man ages, his need for testosterone therapy for hypogonadism increases proportionally. This is due to the natural decline in testosterone production that occurs with aging. 20 percent of the population of men over 60 years of age may have subnormal levels of testosterone compared to when they were younger. That number easily jumps to 30 to 40 percent of males over the age of 80.
In some cases, men in their thirties and forties could find themselves on the receiving end of lower than ideal testosterone levels if they are at the higher end of the decline – losing up to 2 percent of their testosterone each year starting as early as their late twenties.
Testosterone treatment for male hypogonadism can be especially beneficial for someone who cannot or will not make certain lifestyle changes that can help increase testosterone production, including:
- Exercise
- Sleep
- Reduce stress
- Intermittent fasting
- Changing dietary habits
In adults, two types of male hypogonadism occur when the testes do not produce enough testosterone:
- Primary Hypogonadism
This type of hypogonadism originates with the testes and is known as primary testicular failure. Causes may include:
- Cancer treatment such as radiation or chemotherapy
- Testicular injury
- Mumps orchitis
- Hemochromatosis – too much iron in the blood
- Klinefelter syndrome – having 2 or more X chromosomes with one Y chromosome – males should have one of each
- Toxins such as heavy metals and alcohol
- Undescended testicles – often corrects in childhood – if it does not, could lead to Low T
Testosterone replacement therapy for primary hypogonadism is recommended when a man is suffering from the symptoms of Low T.
- Secondary Hypogonadism
Doctors frequently recommend the use of testosterone replacement therapy for secondary hypogonadism since this condition is not due to problems with the testes, but rather with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, as shown below:
- Pituitary gland disorders such as injury, tumor, surgery, or radiation that could impair pituitary function and release of crucial hormones
- Hypothalamus disorders – same as with pituitary gland
- Kallmann syndrome – congenital problem that affects normal development of the hypothalamus
- Medications such as opiates and some hormones can alter testosterone production
- HIV/AIDS can affect the pituitary, hypothalamus, and testes
- Obesity causes the body to convert excess testosterone into estradiol, a form of estrogen that can hinder testosterone production
- Inflammatory diseases such as tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, and histiocytosis
- Illness or surgery, or severe emotional stress
- Normal aging
- Use of hormones illegally and without need
With proper testosterone therapy, secondary hypogonadism is easily treated.
Role of Testosterone in the Treatment of Hypogonadism
The role of testosterone replacement therapy for male hypogonadism treatment becomes clearer to medical science with the release of each new report or study.
Testosterone has benefits that lead to positive changes in the following areas:
Brain functions |
Metabolism |
Cholesterol levels |
Heart health |
Bone and muscle composition |
Quality of life |
Mood and emotional outlook |
Appearance |
Drive and productivity |
Sex life |
Blood cell production |
Energy |
Hair growth |
Insulin and glucose levels |
When using testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadism, a man will be releasing more testosterone into his bloodstream. If he is overweight, or if there is a concern that too much of this testosterone will convert into estradiol via the enzyme aromatase, the doctor may also prescribe an estrogen blocker such as Anastrozole with testosterone treatment for hypogonadism.
Another aspect of treatment includes the use of HCG and clomiphene to restore natural testosterone production by the testes following testosterone replacement therapy for hypogonadism. This ensures that the body picks back up its testosterone secretion after successful treatment of Low T.
Types of Testosterone Therapy for Hypogonadism
Men have numerous options for testosterone replacement in hypogonadism. Each one has its pros and cons, and this decision is not one to enter into lightly or without guidance. Speaking with an experienced hormone specialist can help you make the right choice for your needs.
Options for testosterone replacement therapy for male hypogonadism include:
Testosterone cypionate is the most recommended form of TRT for men, followed by testosterone enanthate – which does not have as long a half-life as cypionate.
Pros – low cost, high effectiveness, best results, longer time between dosing
Cons – possible injection site irritation, fluctuations in testosterone levels
- Testosterone gel
Pros – easy morning application, longer lasting than patches
Cons – expensive, high risk of cross-contamination, skin irritation, avoidance of water for a few hours, no way of knowing how much testosterone is absorbed into bloodstream
- Testosterone patches
Pros – easy to apply once a day, convenient
Cons – very expensive, may fall off and need a new patch, skin irritation, same absorption issue as gel
- Implantable pellets
Pros – lasts for a few months
Cons – expensive surgical procedure, pellet extrusion, fibrosis at implant site, difficult to remove if issues occur
- Transbuccal tablets
Pros – adheres to the gums, twice a day dosing
Cons – expensive, oral irritation, bitter taste to food, uncomfortable, could be swallowed
Finally, the last form of testosterone replacement for hypogonadism is one that doctors do not recommend – oral testosterone. Testosterone that is swallowed could lead to liver toxicity.
To get answers to any questions you have about testosterone therapy and hypogonadism from hormone specialists, please contact Greenberg Health for a free consultation.


















 Norditropin
Norditropin